Stats Behind KEY TO SUCCESS mantra for India
- HouseOfQuality

- Sep 10, 2023
- 2 min read
Updated: Oct 10, 2024
Cricket, often described as a game of glorious uncertainties, is profoundly influenced by numbers and statistics. You would have seen this stat around the Indian cricket team's astonishing 77% win rate when defending scores above 275.
Lets understand the stats behind such claims better in this short blog.

PS : I am a paid subscriber of Disney Hotstar & this image is used for no commercial interest :)
Conditional probability calculates the likelihood of an event occurring given another event has already occurred.
To determine the probability of India winning when setting scores above 275, we follow these steps:
Step 1 : Data collection : Gather details of all ODI matches played by India – India score batting first & Win/Loss.
Step 2 : Count the total number of matches where India set a target above 275 (N).
Step 3 : Count the number of matches within this N where India won (let's call this X).
The conditional probability of India winning when setting scores above 275 is given by:
P(Win | Score > 275) = X/N = 77/100 = 0.77
That was easy-peasy.
Now that we have our calculated probability, how can we determine if this 77% win rate is statistically significant?
What is statistical significance ?
Statistical significance is a crucial concept in data analysis that helps us determine whether an observed effect or difference in data is likely due to a real relationship or if it could have occurred by random chance. Think of it as a way to distinguish between genuine patterns and mere noise in your data.
To assess the statistical significance of the claim that the Indian cricket team has a 77% win rate when it scores above 275, we do a hypothesis test. I have put in some dummy numbers to explain this.
Here's how you can do it using Excel:
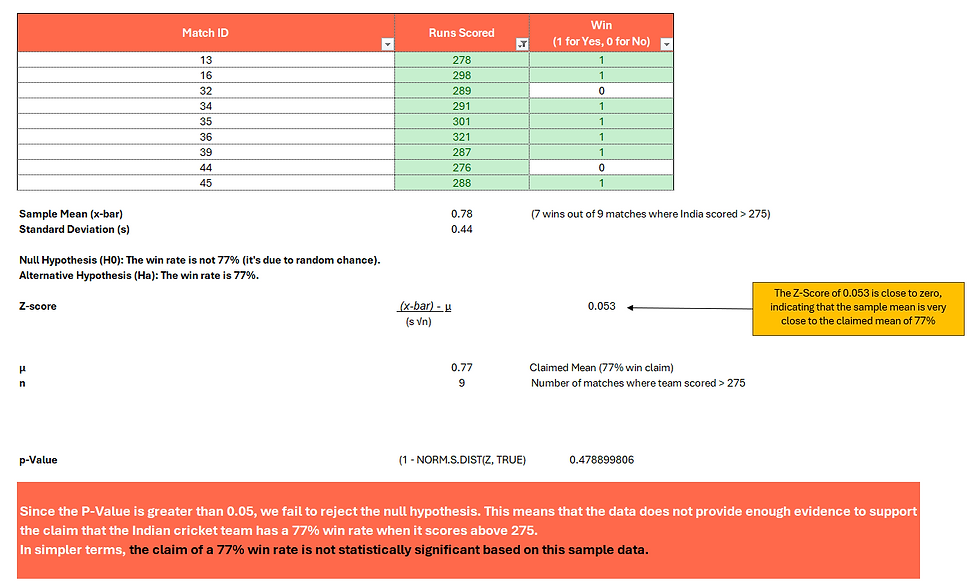
Raw excel sheet -
Statistical concepts are used in all walks of life and this is just one of the many example.
Additional notes :
Minimum Sample Size: Generally, a sample size of at least 30 is considered sufficient for the Central Limit Theorem to kick in, which allows us to make assumptions about the normality of the distribution.
Industry Standards: In some fields, there are guidelines or standards for what constitutes an "adequate" sample size.
Resource Constraints: Sometimes you might be limited by time, money, or data availability.
So, while the sample size of 9 in our example was small, a larger sample size would provide more confidence in the findings. The optimal sample size calculated for hypothesis test, given a 95% confidence level and a 5% margin of error, is approximately 272.
![HouseOf Quality.net (18)[1].png](https://static.wixstatic.com/media/72c1e3_be647acd1ed04c5db567c2601cc2723e~mv2.png)



Comments